Introduction
Light is one of the most powerful external cues that regulate our internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm. In today’s screen-saturated world, understanding how light—especially blue light—affects sleep is crucial to achieving better rest.
1. What Is the Circadian Rhythm?
Our internal 24-hour biological clock.
Governs sleep-wake cycles, hormone production, and metabolism.
Influenced primarily by light and darkness.
2. The Role of Light in Sleep Regulation
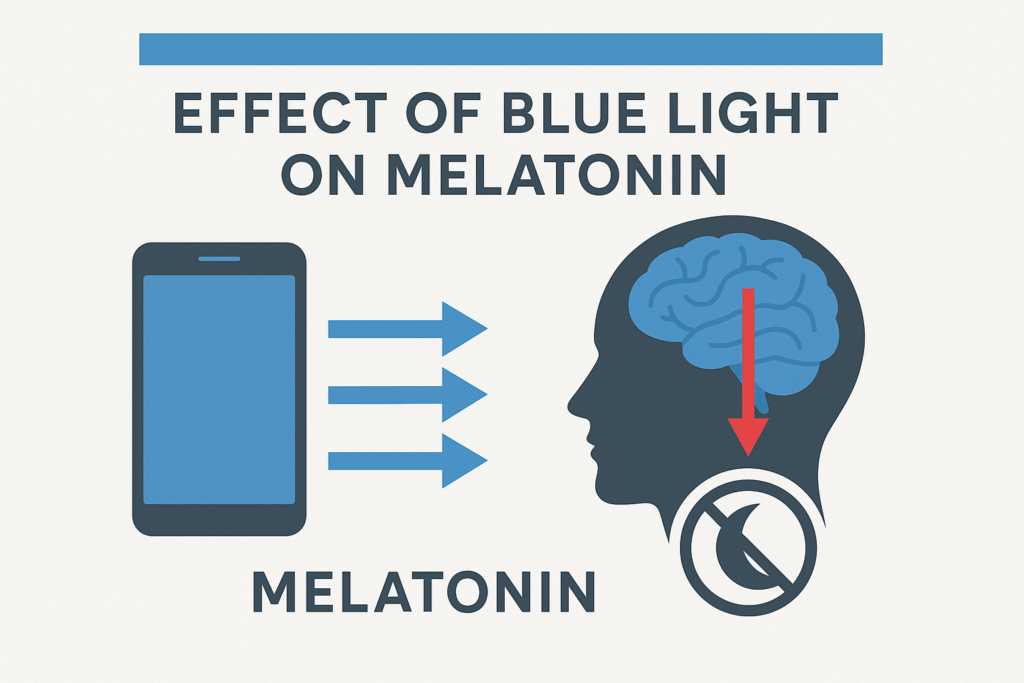
Light enters through the eyes and signals the brain to stay alert.
Melatonin production is suppressed by bright light, especially in the evening.
Natural sunlight exposure in the morning helps reset the sleep cycle.
3. What Is Blue Light?
Short-wavelength, high-energy visible (HEV) light.
Emitted by the sun, but also by phones, computers, and LED lights.
Stronger effect on melatonin suppression than other wavelengths.
4. Blue Light Exposure and Sleep Quality
Exposure after sunset can delay sleep onset.
Reduces total sleep time and REM sleep.
- Disrupts circadian rhythm, leading to insomnia and fatigue.
5. How to Minimize Blue Light Exposure
Use “Night Shift” or “Blue Light Filter” on devices after dark.
Wear blue-light-blocking glasses.
Avoid screens at least one hour before bedtime.
6. Alternatives That Support Sleep
Use warm, amber-colored light bulbs at night.
Increase natural light exposure during the day.
Incorporate sunrise alarms and smart lighting.
7. Summary: Light Hygiene Is Sleep Hygiene
Understanding how light works with your body’s natural rhythms is a major step toward better sleep.
Small daily adjustments can make a big difference.
